Using RANK() and PARTITION BY in SQL Server
By Mike Gledhill
Let's start with a basic query.
Using Microsoft's Northwind sample database, the following script gets a list of Orders placed by a particular Customer, and which Employee placed each of those orders:
SELECT ord.OrderID,
ord.CustomerID,
cst.CompanyName,
ord.EmployeeID,
emp.FirstName + ' ' + emp.LastName AS 'Employee',
ord.OrderDate,
ord.ShipName,
ord.ShipAddress,
ord.ShipCity
FROM Orders ord,
Customers cst,
Employees emp
WHERE ord.CustomerID = cst.CustomerID
AND ord.EmployeeID = emp.EmployeeID
AND ord.CustomerID = 'ALFKI' -- We're just interested in this one customer
ORDER BY ord.CustomerID, ord.EmployeeID, ord.OrderDate DESC
This gives us the following six rows:
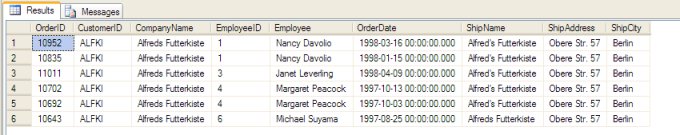
In these six rows, you can see that the Employees "Nancy Davolio" and "Margaret Peacock" placed two orders each. Supposing we now wanted to obtain just the most recent order per employee. How could we do this?
What we need to do is to add a RANK()..PARTITION BY statement. We can get SQL Server to examine each set of records with a distinct CustomerID & EmployeeID combination, and rank them, based on their order dates, with most-recent orders first.
SELECT ord.OrderID,
ord.CustomerID,
cst.CompanyName,
ord.EmployeeID,
emp.FirstName + ' ' + emp.LastName AS 'Employee',
ord.OrderDate,
ord.ShipName,
ord.ShipAddress,
ord.ShipCity,
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY ord.CustomerID, ord.EmployeeID ORDER BY ord.OrderDate DESC) AS 'RankValue'
FROM Orders ord,
Customers cst,
Employees emp
WHERE ord.CustomerID = cst.CustomerID
AND ord.EmployeeID = emp.EmployeeID
AND ord.CustomerID = 'ALFKI'
ORDER BY ord.CustomerID, ord.EmployeeID, ord.OrderDate DESC
Notice how this line adds one extra column of ranking information. For each CustomerID & EmployeeID combination, the most recent Order is the record with a RankValue of 1.
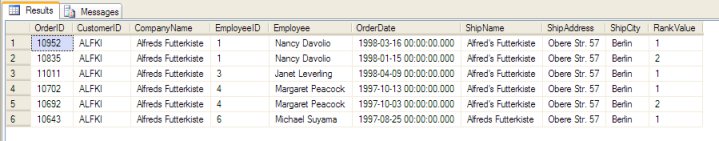
So, to get just the most-recent orders, we need to get a list of records with a RankValue of 1.
Unfortunately, we can't just add this RankValue value to our WHERE clause:
-- This script doesn't work, it'll throw a "Invalid column name 'RankValue'" error.
SELECT ord.OrderID,
...
RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY ord.CustomerID, ord.EmployeeID ORDER BY ord.OrderDate DESC) AS 'RankValue'
FROM Orders ord,
Customers cst,
Employees emp
WHERE ord.CustomerID = cst.CustomerID
AND ord.EmployeeID = emp.EmployeeID
AND ord.CustomerID = 'ALFKI'
AND RankValue = 1
ORDER BY ord.CustomerID, ord.EmployeeID, ord.OrderDate DESC
We need to wrap our entire SELECT into it's own sub-clause, the filter out the RankValue values from there:
SELECT * FROM
(
SELECT ord.OrderID,
ord.CustomerID,
cst.CompanyName,
ord.EmployeeID,
emp.FirstName + ' ' + emp.LastName AS 'Employee',
ord.OrderDate,
ord.ShipName,
ord.ShipAddress,
ord.ShipCity,
Rank() OVER (PARTITION BY ord.CustomerID, ord.EmployeeID ORDER BY ord.OrderDate DESC) as RankValue
FROM Orders ord,
Customers cst,
Employees emp
WHERE ord.CustomerID = cst.CustomerID
AND ord.EmployeeID = emp.EmployeeID
AND ord.CustomerID = 'ALFKI'
) tmp
WHERE RankValue = 1
ORDER BY tmp.CustomerID, tmp.EmployeeID, tmp.OrderDate DESC
And this gives us the most-recent Order, for each CustomerID & EmployeeID.
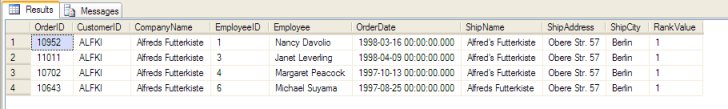
So, my rule of thumb when it comes to using SQL Server ranking is to:
- write your SELECT statement first, to get all records which might be relevant
- add a RANK column, and check that the rank values are working as expected
- then put your SELECT into a sub-query, and filter by the Rank value
Useful links
Sample "Northwind" database for SQL Server 2008
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143221.aspx
Sample "Northwind" database for SQL Server 2000/2005
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=23654
This installs the .mdf and .ldf database files into the directory: C:\SQL Server 2000 Sample Databases
Comments

